Question: What do all of these have in common?
- Delaware Chief Chancellor Andre Bouchard
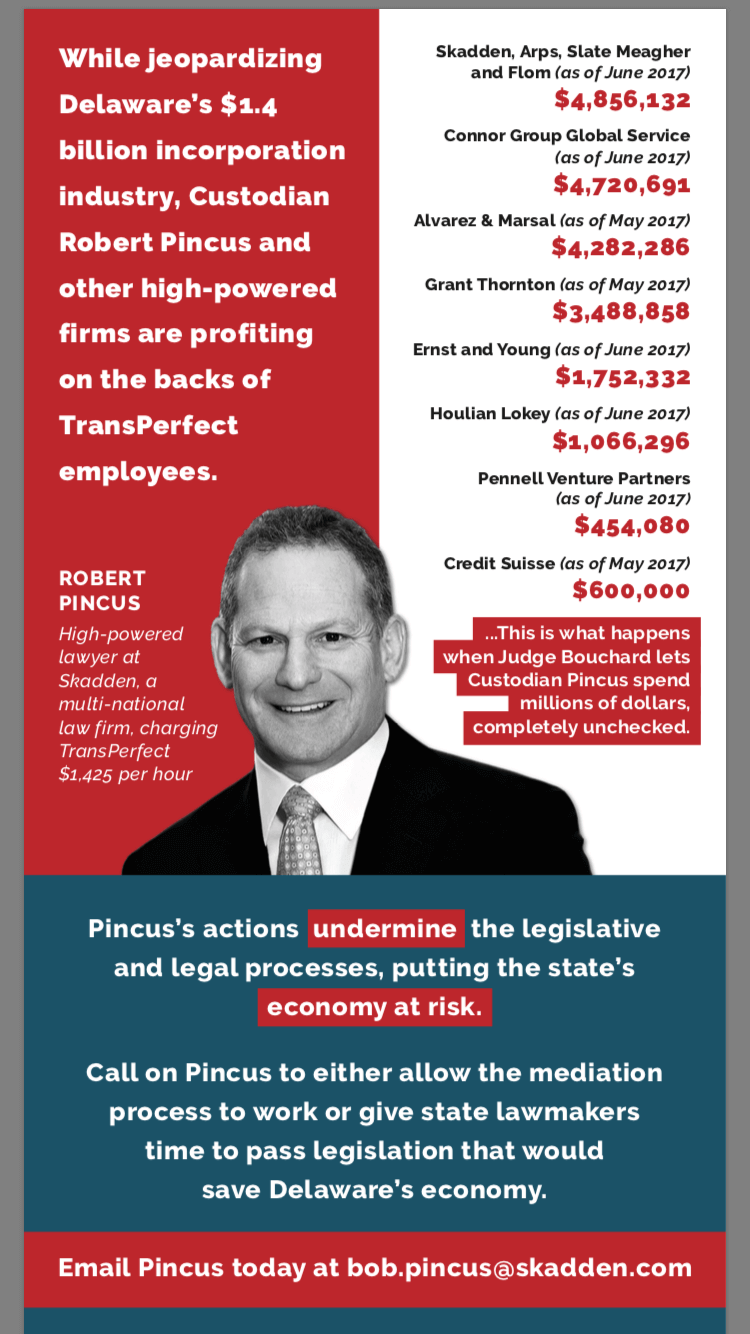
- The $1,425 per hour Court-Appointed TransPerfect Custodian Robert Pincus
- Delaware Supreme Court Chief Justice Leo Strine
- A United States Justice Department investigation into potentially corrupt payments to a large law firm
Answer: Law firm- Skadden Arps.
As Bouchard’s handling of the TransPerfect case melts the main driver of Delaware’s economy (incorporating businesses), it also appears the ice may be melting beneath the feet of legal giant, Skadden Arps.
As I have been calling for an investigation into Bouchard, Bob Pincus and Skadden’s outrageous billing of TransPerfect, The New York Times reported this past Thursday that Skadden Arps is under investigation for potentially corrupt payments from the Ukraine. I hope the investigation spreads to the Wilmington office of Skadden—God knows what they might uncover? I always wondered where Bouchard learned his tradecraft?
Bouchard’s alma mater and Pincus’ current employer were just featured in the New York Times. Apparently, some of Skadden’s fees were shady enough to catch the eye of the Justice Department. And, in my opinion, nothing could be shadier than the Custodian’s TransPerfect bills, which are now rumored at the company to exceed $500,000 per month?!
Here is an actual picture from a Spanish Newspaper of Bob Pincus drowning in money !

Robert Pincus, lawyer partner of the firm Skadden and judicial administrator of Transperfect / FOTOMONTAJE CG
Robert Pincus,
Below is the story as it ran in The New York Times. I’m sure it’s all just an innocent coincidence—or is it?
Your comments are welcome as always,
JUDSON Bennett-Coastal Network
Skadden, Big New York Law Firm, Faces Questions on Work With Manafort
By KENNETH P. VOGEL and ANDREW E. KRAMER
SEPTEMBER 21, 2017
The New York TimesWASHINGTON – Five years ago, Paul Manafort arranged for a prominent New York-based law firm to draft a report that was used by allies of his client, Viktor Yanukovych, the Russia-aligned president of Ukraine, to justify the jailing of a political rival. And now the report is coming back to haunt it.
The Justice Department, according to two people with direct knowledge of the situation, recently asked the firm, Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom, for information and documents related to its work on behalf of Mr. Yanukovych’s government, which crumbled after he fled to Russia under pressure.
The request comes at a time when Mr. Manafort, his work for Mr. Yanukovych’s party and for Russian and Ukrainian oligarchs as well as the handling of payments for that work have become focal points in the investigation of the special counsel, Robert S. Mueller III, into Russian meddling in the 2016 presidential election, and connections between Russia, Mr. Trump and his associates.
It’s unclear if the Justice Department’s request to Skadden, as the firm is known, is part of Mr. Mueller’s inquiry. But the interest from prosecutors in what Skadden did for the Ukrainian government is one indication of the wide-ranging nature of the inquiries related to Mr. Manafort. It also highlights the risks associated with advising authoritarian governments overseas, a lucrative sideline among Washington lawyers, lobbyists and public relations consultants.
Mr. Manafort played a central role in the effort to shield Mr. Yanukovych from international condemnation, according to consultants involved in the effort. He devised the strategy and recruited lobbyists, lawyers and public relations consultants from across the political spectrum, but left the day-to-day implementation of the campaign to others. Skadden’s report was one element of that strategy.
Its conclusions provided a counterpoint to international critics who said that Mr. Yanukovych’s government had prosecuted and convicted the former Ukrainian prime minister, Yulia V. Tymoshenko, on corruption charges in 2011 for political reasons and without sufficient evidence.
That kind of international consulting by American firms traditionally has not drawn much scrutiny from regulators or the media, but that has changed in the last year, thanks largely to Mr. Manafort’s role as Mr. Trump’s campaign chairman in 2016 after years collecting multi-million-dollar paydays from Russian and Ukrainian oligarchs and political parties.
As part of Mr. Mueller’s investigation, prosecutors last month issued grand jury subpoenas seeking testimony from officials from at least two lobbying and public relations firms that worked on the team Mr. Manafort assembled to plead Mr. Yanukovych’s case in Washington – Mercury Public Affairs and the Podesta Group, according to two people with direct knowledge of the subpoenas.
The firms were paid more than $1.1 million each to try to rally support among American policy makers and opinion leaders for Mr. Yanukovych, and the firms’ lobbyists cited the findings in Skadden’s report to quell mounting concerns about his leadership.
The subpoenas for Mercury and Podesta – which followed an earlier round of subpoenas to the firms for documents and information related to their Ukraine work – focused on “Manafort’s money – where it came from, how he got it, what he did with it,” according to a person familiar with the inquiries.
Officials at Mercury and the Podesta Group did not respond to requests for comment.
Through a spokesman, Mr. Manafort declined to comment. Federal agents raided his Virginia home in July, confiscating documents and copying some of his computer files. Shortly afterward, prosecutors working for Mr. Mueller told Mr. Manafort they planned to indict him.
The Justice Department’s request for information about Skadden’s Ukrainian work came after Ukrainian prosecutors asked their American counterparts for assistance in pursuing an inquiry into alleged illegal spending by Mr. Yanukovych’s government. That inquiry included payments to Skadden, though the Ukrainians have not accused the firm of any crime. The Ukrainians nonetheless requested that the Justice Department question Mr. Manafort and Skadden’s lead lawyer on the case, Gregory B. Craig, who had served as President Barack Obama’s White House counsel.
Mr. Manafort’s team hoped that the involvement of Mr. Craig, who maintained deep connections to Washington’s Democratic establishment, might win Mr. Yanukovych a more favorable reception with the Obama State department, according to the consultants who worked on the issue. Yet they said that even employees of Mercury and Podesta regarded the report as a “whitewash” that did little to address valid concerns about Mr. Yanukovych’s government.
The report was concluded in September 2012 – just before one of Mr. Manafort’s daughters started work as an associate at Skadden – and released in December 2012.
The day after its release, Victoria Nuland, a State Department official at the time, called it “incomplete,” at a department press briefing, saying that it “doesn’t give an accurate picture.” She said the State Department was concerned that “Skadden Arps lawyers were obviously not going to find political motivation if they weren’t looking for it.”
In a recent interview, John E. Herbst, a former United States ambassador to Ukraine, went further. He said that Skadden “should have been ashamed” of the report, calling it “a nasty piece of work.”
Mr. Craig declined to comment.
Under the Foreign Agents Registration Act, or F.A.R.A., anyone engaged in lobbying or public relations for foreign governments must register with the Justice Department. But in a statement this month, Skadden contended that “none of our attorneys engaged in any activity that required them or the firm to register under F.A.R.A.”
The firm also asserted that its report “did not opine about whether the prosecution was politically motivated or driven by an improper political objective” – an assertion that narrowly avoids directly contradicting the report’s conclusion that “Tymoshenko has not provided clear and specific evidence of political motivation that would be sufficient to overturn her conviction under American standards.”
Rather, the firm’s statement said that Ms. Tymoshenko “was denied basic rights under Western legal standards,” was “improperly incarcerated during the trial” and that “in the West, she would receive a new trial.”
In June, Skadden refunded $567,000 to the Ukrainian government – about half of the total it was said to have been paid by Mr. Yanukovych’s government. The firm suggested in a statement that it returned the cash because the money had been placed “in escrow for future work” that never took place.
Less than a year and a half after the release of the Skadden report, Mr. Yanukovych fled the country amid street protests over his government’s corruption and its pivot toward Moscow. Under the government that succeeded Mr. Yanukovych, the country’s general prosecutors office – Ukraine’s version of the Justice Department – opened criminal corruption investigations into Mr. Yanukovych and members of his government, including his justice minister, Oleksandr Lavrynovych.
Court documents in the case against Mr. Lavrynovych alleged that Mr. Manafort “designed a strategy” to enlist Skadden to “confirm the legality of the criminal prosecution of Yulia Tymoshenko and … reject any political motives of such prosecution.” Mr. Lavrynovych’s lawyer, Yevgeny V. Solodko, rejected the charges against his client, characterizing the case as a politically motivated crackdown on officials from the former government.
The general prosecutor’s office, under a mutual legal aid agreement with the United States, began asking the Justice Department and the F.B.I. for assistance with the investigation into Mr. Lavrynovych starting in late 2014.
But neither the Justice Department nor the F.B.I. had responded to the requests as recently as March, when the F.B.I. director at the time, James B. Comey, was asked during a congressional hearing why the Ukrainian requests for assistance had gone unheeded.
More recently, Ukraine’s prosecutor general, Yuriy Lutsenko, acknowledged in written responses to The New York Times that his office had begun working with the Justice Department to investigate the payments from the Ukrainian Justice Ministry to Skadden.
Asked whether Ukrainian prosecutors are assisting in Mr. Mueller’s investigation, Mr. Lutsenko’s office was coy. In a statement, it said that it had not publicly disclosed any such cooperation, but it also noted that not all international judicial cooperation can be disclosed.
Representatives for Mr. Mueller’s team and the Justice Department declined to comment.
Kenneth P. Vogel reported from Washington and Andrew E. Kramer from Moscow. Charlie Savage contributed reporting, and Kitty Bennett contributed research.
Kenneth P. Vogel reported from Washington and Andrew E. Kramer from Moscow.
Please note new e-mail address [email protected]